Shipyards faced with vexing capacity issues

Shipbuilding executives have difficult decisions to make about business expansion this decade despite widespread belief that the global merchant fleet will be in urgent need of a major renewal in the coming years.
The number of shipyards has contracted massively from the boom years of the first decade of the 21st century with the sector now far more risk-averse following many years of losses. Nevertheless, many yards are sitting on longer orderbooks than they have enjoyed for many years, with experts predicting an imminent wave of orders for alternative-fuelled ships to replace an aging, polluting global merchant fleet.
According to data from Clarksons Research, today’s shipbuilding capacity is around 40% lower than a decade ago. There are now only 131 large active yards, down from 321 at the peak of the previous shipyard boom in 2009. Clarksons Research’s monitoring of individual facilities suggests only moderate or marginal capacity increases in the medium term. The shipyard forward orderbook cover has edged up to 3.5 years from 2.5 years in 2020 and prices increased 5% across 2022 but were 15% higher on average in 2022 compared to 2021.
In the past few months, Splash has reported on the reopening of shuttered Chinese yards, STX Dalian and Rongsheng, as well as the reopening of Hyundai Heavy Industries’ shipyard in Gunsan in South Korea, while construction of a RMB20bn ($2.76bn) brand new yard has started in northeast China and will be completed by the end of 2024. The new yard, which will be run by Dalian Shipbuilding Industry (DSIC), will focus on LNG carrier construction.
“Although long-term trends point to increasing fleet renewal (besides emissions reduction, fleet age is increasing), 2023 will have its marketing challenges for yards: macro-economic risk is material and may weigh on investor sentiment, alternative fuel choices remain tricky and newbuild prices and berth availability are a hurdle for some owners,” Clarksons Research noted in its most recent weekly report.
Shipbuilders have to balance the global fleet renewal requirements against a backdrop of muted trade growth. The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) predicts for the period 2023–2027 maritime trade growth will expand at an annual average of 2.1%, a slower rate than the previous three-decade average of 3.3%.
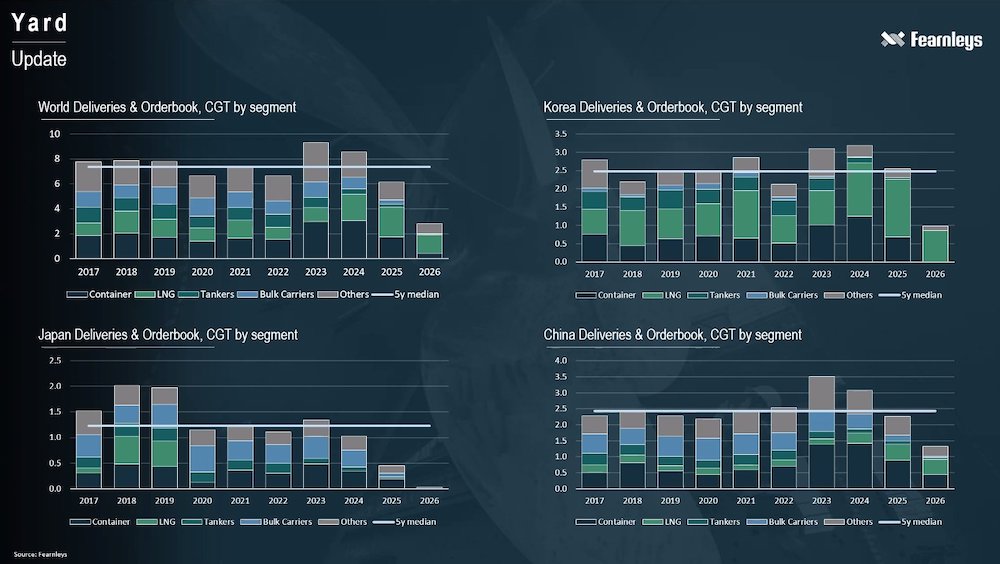
Norwegian broker Fearnleys has also been examining the state of the yards. In a presentation given last week, Dag Kilen, Fearnleys’ global head of research, noted that among Asia’s shipbuilding powerhouses, Japan was the only nation with comparatively early delivery slots at the moment (see slide below).
As the decade progresses, Kilen predicted a shipbuilding bottleneck will emerge, which will be a tailwind for all shipping sectors.
Not everyone is convinced about this potential yard crunch. Danish Ship Finance has argued that further consolidation is on the cards as up to 30% of today’s shipyards are on course to run out of orders soon.
“The lopsided nature of the ordering has created a situation where many of the yards that are not building container or LNG carriers are operating at low utilisation rates. Many are delivering vessels without securing new orders,” Danish Ship Finance pointed out in a recent report, going on to highlight how yard capacity is poorly utilised on average. A group of 95 first-tier yards utilised 70% of their capacity in 2022, according to data from Danish Ship Finance. A more numerous group of second-tier yards only utilised 40% of their capacity in 2022 and will use even less in 2023, Danish Ship Finance forecast, as well as predicting that global yard capacity could shrink by 9m cgt – or 18%- by year-end 2024 if yards that are running out of orders are closed the year after their last delivery.